A new generation of vaccines is on the horizon, thanks to innovative technologies and research breakthroughs. These next-generation vaccines promise to be faster, more effective, and more accessible than ever before, paving the way to better health for people around the world.
One of the most promising areas of research is in the development of mRNA vaccines, which use genetic material to instruct cells to produce proteins that stimulate an immune response. These vaccines use a small piece of genetic material called messenger RNA (mRNA) to instruct cells to produce viral or bacterial proteins that stimulate an immune response. mRNA vaccines do not use weakened or inactivated pathogens,which makes them safer than traditional vaccines. Additionally, mRNA vaccines can be produced faster than traditional vaccines, which is important for responding to rapidly emerging infectious diseases.
These vaccines have been shown to be highly effective against COVID-19 and are being developed for a range of other diseases, including influenza, Zika, and rabies. Self-amplifying RNA vaccines are a type of mRNA vaccine that can replicate themselves once they are inside the body. This allows for a lower dose of vaccine to be used, while still producing a strong immune response.
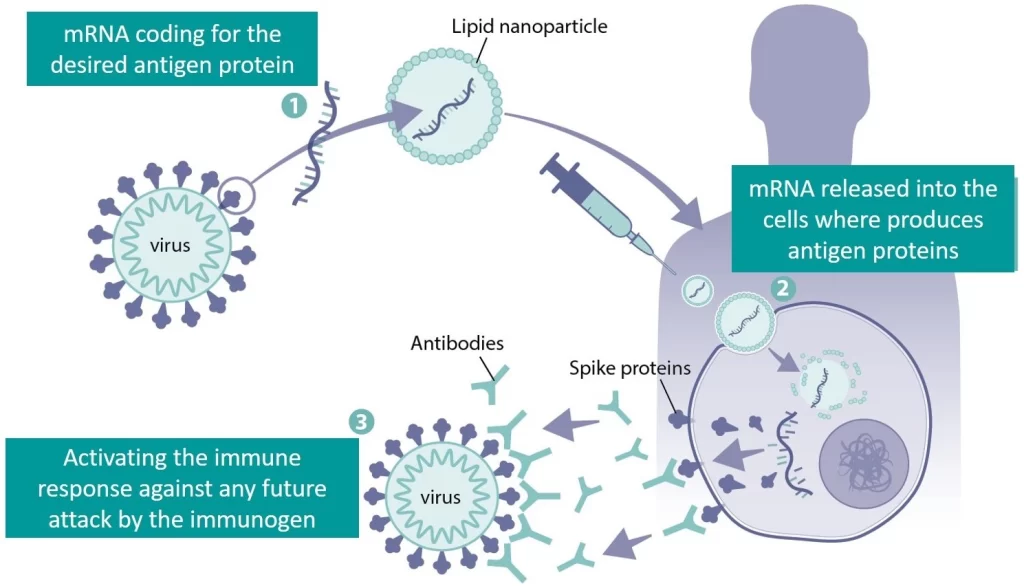
Source: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Another promising approach is the use of nanoparticle vaccines, which use tiny particles to deliver antigens to the immune system. These vaccines are highly versatile and can be used to target a wide range of pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and even cancer cells. The Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, which uses virus-like particles (VLPs) to stimulate an immune response, is one potential illustration of nanoparticle vaccine technology. Clinical trials on the Novavax vaccine showed it to be highly effective, and various nations have approved it for use in emergency situations.
The creation of plant-based vaccinations, which are easier to create and more affordable than conventional vaccines, and the use of T-cell vaccines, which encourage the generation of immune cells with the direct ability to kill infected cells, are other developments. T-cell vaccines are being developed for a range of diseases, including HIV and cancer.
One of the biggest challenges in vaccine development is the need to constantly update vaccines to keep pace with rapidly evolving pathogens. Universal flu vaccines are a potential solution to this problem. These vaccines target highly conserved regions of the influenza virus that do not change as frequently as other regions. This could allow for the development of a vaccine that provides broad protection against multiple strains of the flu.
In addition to these technological advances, the way vaccines are delivered is also changing. For example, needle-free delivery systems are being developed that use high-pressure air to deliver vaccines through the skin, rather than through a needle. This approach is less painful and may also reduce the risk of needle-related injuries.
These game-changing vaccine technologies are paving the way to a new era of vaccine development, one in which vaccines are more effective, accessible, and adaptable to the changing needs of global health. As researchers continue to explore new technologies and refine their use, we can expect to see even more exciting breakthroughs in the field of vaccinology, helping to improve health and save lives for generations to come.